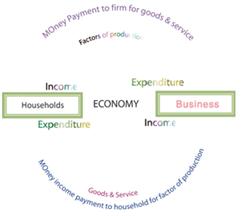
Economics is the study of how societies use scarce resources to produce valuable commodities and distribute them among different people.
Human wants are unlimited, but the resources to satiety these wants are limited. Therefore it is essential to unlimited utilize these limited resources efficiently.
According to Robbins: “Economic is the science which studies human behavior as a relationship between ends and scarce means which have alternative uses.”
Macro economics are the special branch economics knowledge which deals with –
Overall performance of the economics.
The level of social and national output.
The level of employment of the economy.
Mechanism of price level stabilization.
Social consumption and investment
National foreign trade both physical & remittance.
Simply, we can say that macroeconomics is the study of entire economy.
There are three prime objectives of macro – economic –
To increase total output of the economy.
To increase total employment of the economy.
Stabilization of prize level.
Improving the trade balance.